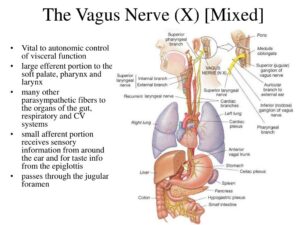
The vagus nerve is an important component of the autonomic nervous system (ANS), specifically the parasympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for regulating involuntary bodily functions like heart rate, digestion, and breathing. It acts as a two-way communication channel between the brain and various organs, influencing everything from heart rate and digestion to immune responses. Respiratory sinus arrhythmia (rytm more accurate! Se also https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3225923/ and https://journals.physiology.org/doi/abs/10.1152/jappl.1960.15.5.863) pattern show how the ANS oscillation function. RSA can be analysed and measured in different ways , e.g. also with Spectral analysis of HR time data series where it is a part of Heart Rate Variability. HRV)
References: ”The autonomic nervous system (ANS) and the immune system are deeply interrelated. The ANS regulates both innate and adaptive immunity through the sympathetic and parasympathetic branches, and an imbalance in this system can determine an altered inflammatory response as typically observed in chronic conditions such as systemic autoimmune diseases. Rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and systemic sclerosis all show a dysfunction of the ANS that is mutually related to the increase in inflammation and cardiovascular risk. Moreover, an interaction between ANS and the gut microbiota has direct effects on inflammation homeostasis. Recently vagal stimulation techniques have emerged as an unprecedented possibility to reduce ANS dysfunction, especially in chronic diseases characterized by pain and a decreased quality of life as well as in chronic inflammation.” https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8910153/#:~:text=The%20ANS%20regulates%20both%20innate,such%20as%20systemic%20autoimmune%20diseases.
https://www.slideserve.com/mercer/the-nervous-system-neural-tissue (no 35)
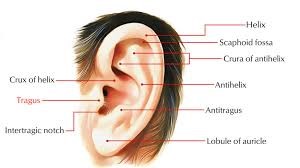
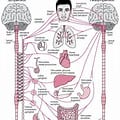
”The vagus nerve, also known as the vagal nerves, are the main nerves of your parasympathetic nervous system. This system controls specific body functions such as your digestion, heart rate and immune system. These functions are involuntary, meaning you can’t consciously control them.
Your left and right vagal nerves contain 75% of your parasympathetic nervous system’s nerve fibers. These fibers send information between your brain, heart and digestive system.
The vagus nerves are the 10th of 12 cranial nerves.
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/22279-vagus-nerve
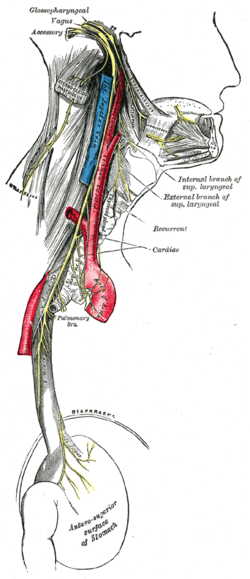
The vagus nerve is the longest cranial nerve in the human body and originates from the elongated marrow in the brainstem. The vagus nerve contains both sensory nerve fibers (from the solitary nucleus and the spinal nucleus of the triplet nerve) and motor nerve fibers (from the dorsal vagus nucleus and the ambiguus nucleus). The vagus nerve consists of about 80,000 nerve fibers, 80 percent of which consists of collecting data about what is going on in the body, and 20 percent of the activity is used to control processes in the body.
The vagus nerve is important in both the autonomic and somatic nervous systems. The autonomic nervous system can be divided into visceral afferus (visceral sensory) and visceral effervescent (visceral motor skills, here parasympathetic). The vagus nerve only innervates sensorially within the somatic nervous system (somatoafferens). In addition to this, the vagus nerve also contains so-called brankial-efferent nerve fibers that innervate skeletal muscle that embryologically originates from the gill arches of the gill apparatus[1][2][3]. https://sv.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vagusnerven
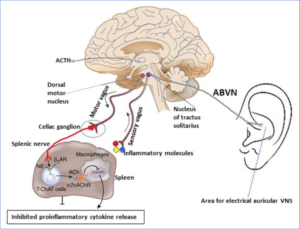
Fig above The inflammatory reflex and how transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation may activate the pathway. Afferent vagus nerve fibers residing in the nodose ganglion are stimulated in the periphery by damageassociated molecular pattern molecules (DAMPs), including cytokines, and pathogen-associated molecular pattern molecules (PAMPs). The signals are transmitted to the nucleus of tractus solitarius (NTS). Reciprocal connections between the NTS and the dorsal motor nucleus (DMN) of the vagus mediate communication with and activation of efferent vagus fibers (motor vagus) from the DMN. The signal is propagated to the celiac ganglia, where the splenic nerve originates. Norepinephrine (NE) released from the splenic nerve interacts with beta2-adrenergic receptors (beta2-AR) on certain splenic T lymphocytes and causes the release of acetylcholine (ACh) from T cells containing choline acetyltransferase (TChAT cells). ACh interacts with a7-subunit-nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (a7nAChR) on macrophages and inhibits proinflammatory cytokine production and inflammation. Transcutaneous electrical stimulation of the auricular branch of the vagus nerve (ABVN) in the left ear also signals to the NTS and thus activates efferent vagus signals to the splenic TChAT cells. Abbreviations not explained in the text: ACTH= adrenocorticotropic hormone; VNS=vagus nerve stimulation.
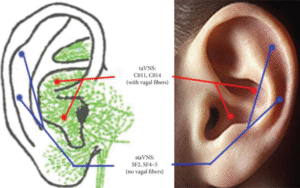
Fig 2 Caption – The innervations of the auricular branch of the vagal nerve and the points stimulated at the ear. The vagal nerve branch is marked by green color, the taVNS points by red, and the staVNS points by blue. False.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/347589598_The_Instant_Effects_of_Continuous_Transcutaneous_Auricular_Vagus_Nerve_Stimulation_at_Acupoints_on_the_Functional_Connectivity_of_Amygdala_in_Migraine_without_Aura_A_Preliminary_Study/figures?lo=1
BvS-> BUT – NB massage at the two red Points at the picture might be as effective, given you find out how to massage them – a kind of acupressure.
Vagus is our ”wandering nerv”, which together with GABA is our most important inhibitory functions. Pattern of Parasympathetic and Sympathetic oscillation can we measure and see in Respiratory Sinus (Arrhythmia, RSA) Rhythm (more correct while this is not actually an arrhythmia, but still called RSA.
A lot of inspiration can be found in Eastern traditional medicine, Chi Kung, e.g. beating the heavenly drum
”This technique, known as ‘banging the heavenly drum’ or ‘sound the heavenly drum’ (Ming Tian Gu), and is used to wake up your brain and stimulates your thinking processes. Beating the drum clears the mind, wakes up the brain and enhances your cognitive faculties. It is very useful when feeling your energy or concentration flagging and is also said to improve your hearing. When you are finished and take your hands off your ears and enjoy feeling like you just woke up refreshed and ready to work.” https://inspireportal.com/the-tao-of-creativity-taoist-tools-to-help-your-writing-and-creative-work/
Reference: The Complete System of Self Healing. Internal Exercises 1986 Stephen Chang, https://www.gettextbooks.com/isbn/9780894070174/
“Tap gently on your index finger with the same hand’s middle finger, in a slow steady rhythm. Tap 12, 24 or 36 times and then release the fingers from the ears and rest. Tap both ears simultaneously or alternatively on each ear. Repeat the cycle three times. Ideally, you need to do this exercise one to three times a day, depending on the severity of ear ringing”. https://allendaleacupuncture.com/2018/04/20/beating-the-heavenly-drum-qigong-exercise/
See also https://carism.se/2021-2023/my-experimental-intervention-work/nytt-perspektiv-pa-svar-tinnitus/
Swedish
See picture above (th first)
Fig 1. Den inflammatoriska reflexen och hur transkutan aurikulär vagusnervstimulering kan aktivera vägen. Afferenta vagusnervfibrer som finns i nodosgangliet stimuleras i periferin av skadeassocierade molekylära mönstermolekyler (DAMPs), inklusive cytokiner, och patogenassocierade molekylära mönstermolekyler (PAMPs). Signalerna överförs till kärnan i tractus solitarius (NTS). Ömsesidiga kopplingar mellan NTS och den dorsalmotoriska kärnan (DMN) i vagus förmedlar kommunikation med och aktivering av efferenta vagusfibrer (motorvagus) från DMN. Signalen sprids till celiaki ganglierna, där mjältnerven har sitt ursprung. Noradrenalin (NE) frisatt från mjältnerven interagerar med beta2-adrenerga receptorer (beta2-AR) på vissa T-lymfocyter i mjälten och orsakar frisättning av acetylkolin (ACh) från T-celler som innehåller kolinacetyltransferas (TChAT-celler). ACh interagerar med a7-subunit-nikotinacetylkolinreceptorer (a7nAChR) på makrofager och hämmar proinflammatorisk cytokinproduktion och inflammation. Transkutan elektrisk stimulering av den aurikulära grenen av vagusnerven (ABVN) i vänster öra signalerar också till NTS och aktiverar därmed efferenta vagussignaler till mjältens TChAT-celler. Förkortningar som inte förklaras i texten: ACTH= adrenokortikotropt hormon; VNS=vagusnervstimulering.

Fig 2 Bildtext – Innervationerna av den aurikulära grenen av vagusnerven och de punkter som stimuleras vid örat. Den vagala nervgrenen är markerad med grön färg, taVNS-punkterna med röd och staVNS-punkterna med blå. Falsk.
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/347589598_The_Instant_Effects_of_Continuous_Transcutaneous_Auricular_Vagus_Nerve_Stimulation_at_Acupoints_on_the_Functional_Connectivity_of_Amygdala_in_Migraine_without_Aura_A_Preliminary_Study/figures?lo=1.
BvS-> MEN – OBS massage på de två röda punkterna på bilden kan vara lika effektivt, förutsatt att du får reda på hur du ska massera dem – en slags akupressur.
Vagus är vår ”vandrande nerv”, som tillsammans med GABA är våra viktigaste hämmande funktioner. Mönster av parasympatisk och sympatisk svängning kan vi mäta och se i Respiratory Sinus (Arrhythmia, RSA) Rhythm (mer korrekt även om detta faktiskt inte är en arytmi, men ändå kallas RSA.
Mycket inspiration finns att hitta inom österländska traditionell medicin, t.ex. slå på den himmelska trumman
”This technique, known as ‘banging the heavenly drum’ or ‘sound the heavenly drum’ (Ming Tian Gu), and is used to wake up your brain and stimulates your thinking processes. Beating the drum clears the mind, wakes up the brain and enhances your cognitive faculties. It is very useful when feeling your energy or concentration flagging and is also said to improve your hearing. When you are finished and take your hands off your ears and enjoy feeling like you just woke up refreshed and ready to work.” https://inspireportal.com/the-tao-of-creativity-taoist-tools-to-help-your-writing-and-creative-work/
Referens: Det kompletta systemet för självläkning. Interna övningar 1986 Stephen Chang, https://www.gettextbooks.com/isbn/9780894070174/
“Tap gently on your index finger with the same hand’s middle finger, in a slow steady rhythm. Tap 12, 24 or 36 times and then release the fingers from the ears and rest. Tap both ears simultaneously or alternatively on each ear. Repeat the cycle three times. Ideally, you need to do this exercise one to three times a day, depending on the severity of ear ringing”. https://allendaleacupuncture.com/2018/04/20/beating-the-heavenly-drum-qigong-exercise/
See also https://carism.se/2021-2023/my-experimental-intervention-work/nytt-perspektiv-pa-svar-tinnitus/
BvS 2022-05-18